Early detection in firstborn children could give parents the opportunity to decide if they want to have more kids, with previous studies indicating an increased likelihood siblings of autistic children are more likely to develop the disorder.
“Detection inevitably changes family dynamics and goals, and creates consideration about the time required to help the child,
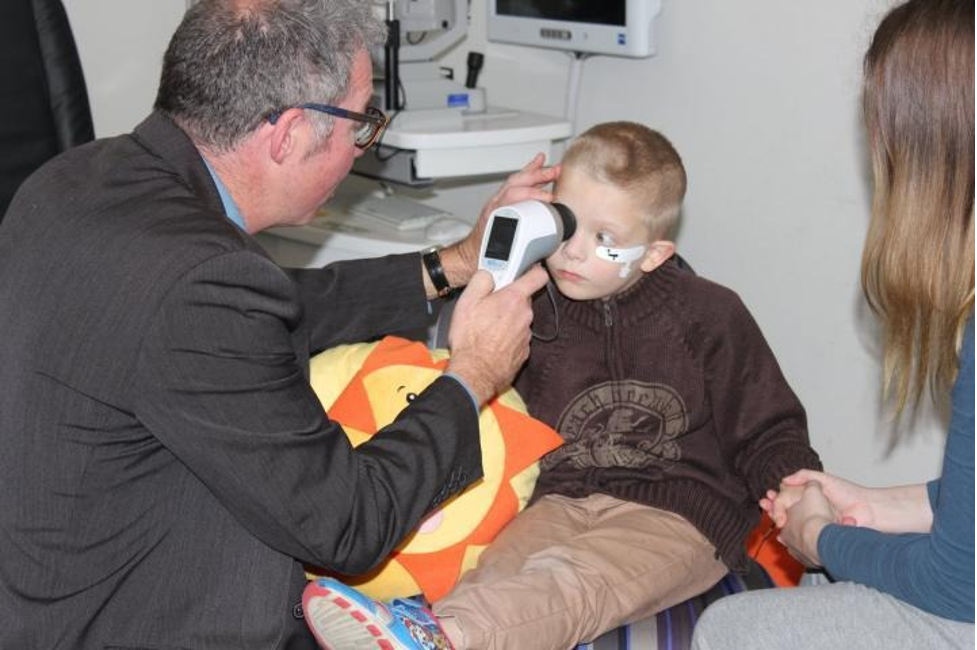
The non-invasive eye scan utilizes a hand-held device to find a pattern of subtle electrical signals in the retina that are different in children on the autism spectrum, which are directly linked to differences in their brain development.
The scan was tested on about 180 people with and without autism between the ages of 5 and 21 in collaboration with Yale University in the US, University College London and Great Ormond Street Hospital in the UK, as part of a study published in the Journal of Autism and Developmental Disorders.
These potential biomarkers for autism spectrum disorder (ASD) could allow for early detection of other disorders, such as attention deficit hyperactivity disorder (ADHD).
Dr Paul Constable, a senior lecturer at the College of Nursing and Health Sciences at Flinders University, has been searching for an autism “biomarker” since 2006, in an effort to improve early detection and intervention methods after his own child was diagnosed.
“The retina is an extension of the brain, made of neural tissue and connected to the brain by the optic nerve, so it was an ideal place to look,” says Dr Constable.
“The test is a quick, non-intrusive eye-scan using a hand-held device and we anticipate it will be equally effective on younger children. Very early diagnosis means not only can children receive important interventions, but families are empowered to get the necessary supports in place, come to terms with the diagnosis, and make informed decisions.”
Dr Constable’s research team is also investigating the scan to detect autism in younger children and other conditions including attention deficit hyperactivity disorder, and other neurodevelopmental disorders.
“Now we have found a likely candidate biomarker for autism, the next stage is to look at young children, even infants, as the earlier we can get to intervention stages the better,” Dr Constable says.
He says his team often encounters parents who have two or three young children with autism, as the chance of having a second autistic child is much higher for parents with one child on the spectrum.
In another researcher published in march2021 in Reuters a Hong Kong scientist has developed a method to use machine learning and artificial intelligence to scan retinas of children as young as six to detect early autism or the risk of autism and hopes to develop a commercial product this year.
Retinal eye scanning can help to improve early detection and treatment outcomes for children, said Benny Zee, a professor at the Chinese University of Hong Kong.
“The importance of starting early intervention is that they are still growing, they are still developing. So there is a bigger chance of success,” Zee said. His method uses a high-resolution camera with new computer software which analyses a combination of factors including fibre layers and blood vessels in the eye.
The technology can be used to identify children at risk of autism and get them into treatment programmes sooner, said Zee.
Seventy children were tested using the technology, 46 with autism and a control group of 24. The technology was able to identify the children with autism 95.7 percent of the time. The average age tested was 13, with the youngest being six. Zee’s findings have been published in EClinicalMedicine, a peer-reviewed medical journal.
Autism specialists welcomed his findings but said there remained a huge stigma, with parents often reluctant to believe their children have autism even when there are clear signs.
Resources:
https:eurekalert.org/pub_releases/.2020-02/fu-aes022020.phb
https://mobile.reuters.com/article/.amp/iduskbn2b702l
IMUTISM Team